The Mechanical Lateral Distal Femoral Angle in Thai Patients With Varus Knee Osteoarthritis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56929/jseaortho-2025-0265Keywords:
varus deformity osteoarthritis, mechanical lateral distal femoral angle, hip-knee-ankle angle, joint line convergence angleAbstract
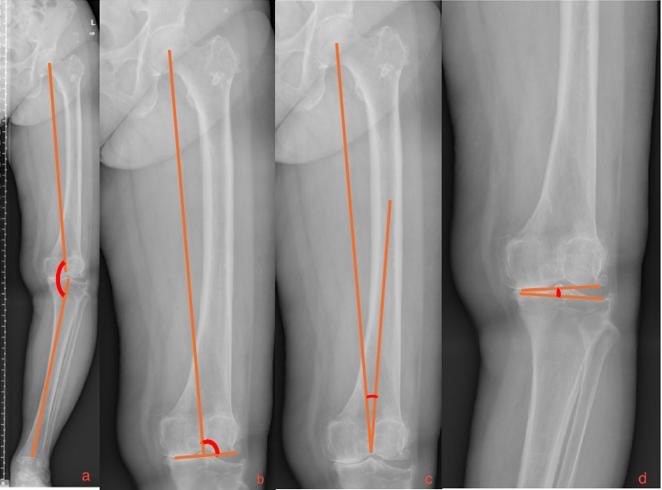
Purpose: Varus deformity is commonly observed in knee osteoarthritis (OA) and involves medial compartment degeneration, bone morphologic changes, soft tissue balance, and may complicate mechanical alignment during total knee arthroplasty (TKA), especially involving conventional alignment techniques. We evaluated the distribution of mechanical lateral distal femoral angle (mLDFA) and its association with coronal alignment parameters in Thai patients with varus knee OA to improve preoperative planning.
Methods: Patients with varus knee OA who underwent preoperative orthoroentgenographic imaging between 2020 and 2023 were retrospectively stratified into three mLDFA-based groups (<90° [A], 90° [B], >90° [C]) to compare differences in hip-knee-ankle angle (HKAA), joint line convergence angle (JLCA), and mechanically aligned-anatomical angle (MA-AA).
Results: mLDFA prevalence was determined in 444 patients (Group-wise: A=56.3%; B=28.7%; C=14.9%). Group A had smaller MA-AA values (5.38° ± 1.44°) compared with Group C (6.74° ± 1.69°, p < 0.001). Increased mLDFA values were associated with reduced HKAA values, while mLDFA values positively correlated with those of MA-AA. The mean JLCA value was significantly higher in patients with HKAA <170° compared with those with HKAA ≥170° (7.14° vs. 3.83°, p < 0.001). A JLCA value ≥10° was more prevalent in patients with HKAA <170° (18.2%) than in those with HKAA >170° (0.35%).
Conclusion: Increased mLDFA and MA-AA values were associated with more severe varus deformity (showed reduced HKAA values), indicating a need to individualize distal femoral valgus correction during TKA for patients with severe varus deformity. Preoperative mLDFA assessment may optimize alignment and surgical outcomes.
References
Matsuda S, Miura H, Nagamine R, et al. Effect of femoral and tibial component position on patella tracking following total knee arthroplasty: 10-year follow-up of Miller-Galante I knees. Am J Knee Surg 2001;14:152-6.
Liau JJ, Cheng CK, Huang CH, et al. The effect of malalignment on stresses in polyethylene component of total knee prosthesis: a finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol) 2002;17:140-6.
Windsor RE, Scuderi GR, Moran MC, et al. Mechanisms of failure of the femoral and tibial components in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1989;(248):15-9.
Tew M, Waugh W. Tibiofemoral alignment and the results of knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1985;67:551-6.
Jeffrey RS, Morris RW, Denham RA. Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1991;73:709-14.
Shelton TJ, Gill M, Athwal G, et al. Outcomes in patients with a calipered kinematically aligned TKA that already had a contralateral mechanically aligned TKA. J Knee Surg 2021;34:87-93.
Bourne RB, Chesworth BM, Davis AM, et al. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty: who is satisfied and who is not?. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010;468:57-63.
Winnock de Grave P, Luyckx T, Claeys K, et al. Higher satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty using restricted inverse kinematic alignment compared to adjusted mechanical alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2022;30:488-99.
Songkiat P, Pacharapol U. The coronal angulation of the femur in Thai osteoarthritic knee patients with varus deformity. Siriraj Med J 2011;63:156-9.
Lin YH, Chang FS, Chou KH, et al. Mismatch between femur and tibia coronal alignment in the knee joint: classification of five lower limb types according to femoral and tibial mechanical alignment. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2018;19:411.
Meng C, Li C, Xu Y. Progress in computer-assisted navigation for total knee arthroplasty in treating knee osteoarthritis with extra-articular deformity. Orthop Surg 2024;16:2608-19.
Rattanaprichavej P, Laoruengthana A. Accelerometer-based navigation versus conventional total knee arthroplasty for posttraumatic knee osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Surg 2022;14:522-8.
Charaya H, Gill HS, Bhan R. Functional outcome based on mechanical axis alignment following total knee arthroplasty. Cureus 2022;14:e22553.
Chotanaphuti T, Ongnamthip P, Teeraleekul K, et al. Comparative study between computer assisted-navigation and conventional technique in minimally invasive surgery total knee arthroplasty: prospective control study. J Med Assoc Thai 2008;91:1382-8.
Saradej K, Siripat P, Danai H, et al. Comparison between image-free robotic assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty: postoperative CT assessment of alignment. J Southeast Asian Med Res 2020;4:16-23.
Thanainit C, Visit W, Saradej K, et al. The accuracy of component alignment in custom cutting blocks compared with conventional total knee arthroplasty instrumentation: Prospective control trial. Knee 2014;21:185-8.
Chaudhary C, Kothari U, Shah S, et al. Functional and clinical outcomes of total knee arthroplasty: a prospective study. Cureus 2024;16:e52415.
Pauzenberger L, Munz M, Brandl G, et al. Patient-specific instrumentation improved three-dimensional accuracy in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res 2019;14:437.
MacDessi SJ, Jang B, Harris IA, et al. A comparison of alignment using patient-specific guides, computer navigation and conventional instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. Knee 2014;21:406-9.
Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, et al. Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2010;92:2143-9.
Dossett HG, Arthur JR, Makovicka JL, et al. A randomized controlled trial of kinematically and mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasties: long-term follow-up. J Arthroplasty 2023;38:S209-14.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The Royal College of Orthopaedic Surgeons of Thailand

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






